Blockchain is essentially a chain of blocks with information inside it. This method was first discovered in 1991 by a group of scientists. They aimed to use it as timestamps of digital documents so that they cannot be backdated or tampered with. But this method came into its real use when Satoshi Nakamoto used it to build Bitcoin.
Blockchain technology is transforming a range of sectors such as crypto, supply chain and logistics, education, energy sector, real estate, and many others. Similarly, blockchain technology in banking is leading its digital transformation. It is enhancing banking features like security, transparency, and efficiency. Banking systems have remained unchanged for decades now, but blockchain in finance is changing them very fast.
In this guide, we will explore in detail blockchain in banking. What exactly is blockchain technology, blockchain in banking, some case studies, and blockchain future in banking are the things that we will present in detail.
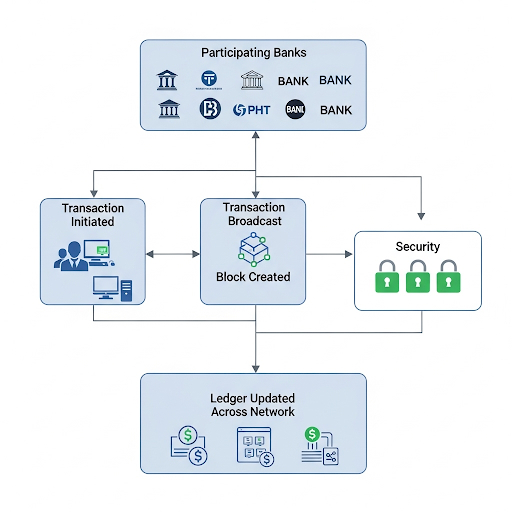
What Exactly is Blockchain?
Blockchain has become one of the most thrown-around buzzwords of current times. Blockchain records transactions across multiple user platforms so that they are tamper-proof. It is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology.
Each block of a blockchain contains three things: data, hash, and the hash of the previous block. Inclusion of a back hash is the key to security and immutability for the blockchain. The following are the key features of blockchain that are attractive for the banking sector.
Decentralization: By nature, blockchain is decentralized, and hence it is resistant to single-point failure and control
Transparency: Every user on the blockchain can validate the transaction, making the system fully transparent
Immutability: Once recorded on the blockchain, data cannot be modified, rendering fraudulent schemes virtually impossible
Smart Contracts: Blockchain supports self-executing contracts, which saves time and eliminates human errors.
Security: All the dealings on blockchain are encrypted, making it impossible for unauthorized alteration
Why Blockchain in Banking?
Traditional banking has systems and practices that are old and time-tested. All these banking practices in place make banking work all over the world, but it has its challenges. These challenges include:
· High transaction costs
· Slow cross-border payments
· Vulnerable to fraud and other security risks
· Lack of transparency
All of these issues can be addressed by blockchain technology in banking in the following ways:
Faster Cross-Border Payment with Reduced Cost
Our traditional banking system, “SWIFT,” takes days to transfer money and involves multiple intermediaries. Blockchain in banking promises near-instant transfers with a fraction of the cost without the intervention of any intermediary. Real-time cross-border transactions in a seamless manner are already being enabled by Ripple (XRP) and Stellar.
Enhanced Security & Fraud Prevention
As security is decentralized and every user authenticates each transaction, blockchain in banking minimizes the fraud risks. This offered security is one of the key features of blockchain technology in banking.
Transparency with Auditability
Blockchain is a ledger-based technology where every transaction is recorded. So, auditors can verify every record of financial flow in real time. This ensures maximum transparency.
Automated Banking
Blockchain supports automated smart contracts. These automated contracts can include loan approvals, trade settlements, or compliance checks. This eliminates human intervention, thus minimizing the cost and human errors.
Lower Operational Costs
Since blockchain technology in banking doesn’t rely on human interventions much, it cuts the overhead costs. Think of it as a complete removal of reconciliation, compliance, and fraud management sections of traditional banking.
With all these lucrative benefits offered by the blockchain in banking, this technology might take over traditional banking sooner than we anticipate.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Banking
There are multiple use cases of blockchain in banking that have already been implemented or are being pursued rigorously.
Payments and Remittances
· RippleNet: Enabling banks to settle financial transactions in seconds
· JPM Coin: Developed by JPMorgan, it facilitates instant institutional payments.
Trade Finance
· Letter of Credit (LC) Automation: Blockchain in banking digitizes the documents, which ultimately reduces delays and improves security
· Komgo & Contor: They streamline trade finance with blockchain-based platforms
Identity Verification (KYC/AML)
· Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI): This allows customers to securely control their identity-related data
· HSBC & Deutsche Bank: These renowned banks are using blockchain for KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance, which reduces duplication
Securities Settlement
· Tokenized Assets: It enables fractional ownership with faster settlements
· Depository Trust and Clearing Corporation (DTCC): It uses blockchain for clearing and settlement
Digital Identity
· Blockchain, with its secure and user-controlled digital identities, helps prevent identity theft. It also streamlines the customer authentication.
Fraud Detection
· With everything digitized, blockchain analytics detects and flags any suspicious transactions in real time.
Case Studies of Blockchain in Banking
Multiple renowned financial institutions are taking the lead in the banking blockchain revolution.
JP Morgan Chase: To enhance the interbank payments, they developed Quorum, a permissioned blockchain. Till now, they have processed billions in transactions with enhanced speed and transparency.
Santander: They launched a remittance service that was blockchain-based. It enabled the same-day cross-border transactions with reduced costs.
HSBC: They settled a $250 billion foreign exchange transaction back in 2021 by using blockchain. This reduced settlement risks and operational costs.
Challenges of Blockchain Implementation in Banking
With all the benefits that blockchain technology in banking has to offer, it still has multiple implementation challenges.
1. Regulatory Uncertainty: The banking system is connected worldwide, but different countries have different laws and perspectives for blockchain. This makes cross-border banking a big challenge. There is a need for cross-country partnerships and cooperation to develop a clear central legal framework in order for the blockchain in banking to work.
2. Scalability Issues: Public blockchains often struggle to keep up with high traffic, especially during busy periods. Worldwide banking is a whole new level for these public blockchains. Scalability concerns must be addressed for blockchain to go global, banking-wise.
3. Legacy Systems Integration: With the decade-old legacy systems of traditional banking, blockchain integration is both financially and technically challenging to achieve. As traditional systems are centralized, while blockchain is decentralized so major process overhauls are required.
4. Energy Consumption: A significant amount of energy is consumed by the Proof-of-Work blockchains like Bitcoin due to the massive required computations. Banks prefer the energy efficiency alternative to maintain their sustainability goals. So environmental concerns attached to the energy provision to blockchain also need addressing.
All these challenges require complete focus and wider cooperation for blockchain in banking to excel.
Future of Blockchain in Banking
Many future blockchain trends are accelerating the adoption in banking.
1. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): CBDCs create secure government-backed digital currencies using blockchain. While maintaining central bank control, they modernize the payment systems. Currently, over 130 countries are exploring CBDCs, for example Digital Euro and the Digital Yuan.
2. Interoperability Between Blockchains: Polkadot and Cosmos are enabling seamless cross-chain transactions. Seamless communication among blockchain networks is a necessity for cross-border payments for multiplatform services.
3. Hybrid Blockchain Models: To address the transparency and privacy balance, banks are combining the public and private blockchains. This way, banks can enjoy the benefits of decentralization with the flexibility for regulatory compliance.
4. AI & Blockchain Integration: Integrating AI with blockchain can make it more secure and efficient with features like fraud detection, credit scoring, and risk assessment.
5. Tokenization of Assets: Real-world assets like bonds, real estate, and other commodities can be tokenized. This will enable fractional ownership with faster settlements.
Blockchain in banking, driven by the advancements in scalability, regulation, and integration, can enable the fintech market to reach $49.2 billion by 2030.
Important Blockchain Considerations for Banks
Banks that aspire to embrace the blockchain in banking should consider the following:
1. Feasibility Studies: Banks should evaluate their potential use cases with high ROI and necessary regulatory compliance.
2. The Right Blockchain Model: Depending on the required control needs and privacy, banks should choose between public, private, or consortium blockchains accordingly.
3. Engaging with the Regulatory Body: Banks should engage with the related regulatory body early to ensure compliance and to build trust.
4. HR Investment: Banks should hire and train existing staff on blockchain developments, cryptography, and cybersecurity.
5. Scalability: Banks should plan for scalability to make sure that their current solution can handle the ever-growing transaction volumes.
Conclusion
Blockchain in banking is not another technological advancement for the sector, but it is a fundamental shift for the entire sector. It will change how the whole financial world operates. Blockchain technology in banking promises to address the long-standing issues of traditional banking, which include challenges of cost, speed, security, and trust.
It offers a secure, transparent, and efficient transaction solution that will surely improve our banking system. There are some hurdles like regulation compliance, integration, and scalability issues, but blockchain technology in banking is being adopted at an increased pace.
Many industry leaders are leading from the front, this financial revolution like JP Morgan, Santander, and HSBC. Such banks and financial institutions will surely have an advantage over their competitors in the future when it comes to speed, security, transparency, cost, and trust.