Are you handling large data volumes with increasing workload? Your system should be highly flexible as scalability is crucial for maintaining the system’s performance. It becomes more valuable when the demand increases and you need a speedy system to operate all functions smoothly.
In this article, we will shed light on the database design patterns for scalable applications. We will discuss the importance of a scalable database, who needs it, and what the best practices are for database design patterns. Let’s begin to explore!
What is a Scalable Database?
When I talk about scalable databases, it refers to the ability of a database to handle heavy workloads and traffic without compromising response time. A scalable database can accommodate large amounts of data without compromising performance.
When a company is scaling, it is trying to extend the size, amount, or importance of something. Hence a speedy and managed database is necessary for good performance of a system.
Why is it Important to have a Scalable Database?
It is necessary to have a scalable database for many reasons. These are as follows:
- It handles increasing data volumes and manages user demands.
- It offers a cost-effective solution by granting resources.
- It prevents bottlenecks and slow processing.
- It maintains fast response time and consistency in performance.
- It can handle unexpected surges in traffic without crashing.
- It improves the user experience by availability and contributes to their satisfaction and retention.
- It provides agility to adapt to changes in the future so that the infrastructure supports the business in the long term.
In short, database design patterns are important for a business to accelerate the user experience and growth according to increasing demands.
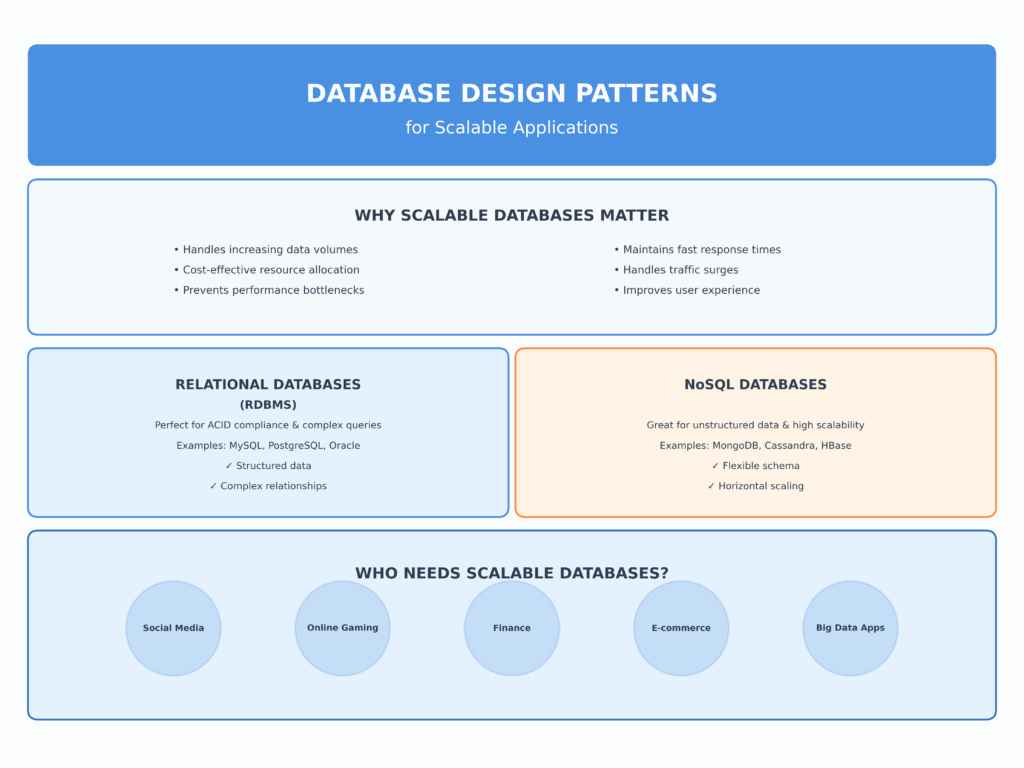
Who Needs a Scalable Database?
Businesses dealing with large volumes of data such as e-commerce, social media, finance, and gaming need scalable database design patterns to avoid performance bottlenecks, high-cost, and crashes. For instance, you need a scalable database to experience peak loads without a collapsing system.
Industries that Need Scalable Databases
If you are running one of these industries, you probably need a scalable database.
- Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms have large volumes of data and manage interactions with many users at the same time.
- Online Gaming
It supports a large number of player bases, real-time game data, and high transaction data at the same time.
- Applications with a Great Deal of Data
Those applications that generate large amounts of data need scalable applications to handle them efficiently.
- E-commerce Platforms
Online shopping platforms handle unexpected customer traffic, especially during sales, events, or holidays. A scalable database is required to run the system effectively without any disruption.
- Finance
Dealing with large amounts of transactions, financial data and customer accounts must have stable and efficient database design patterns.
If you are dealing with one of these kinds of applications, you need to know how you can implement a scalable database for your system. Learn how we at Objects help you achieve remarkable results with our services.
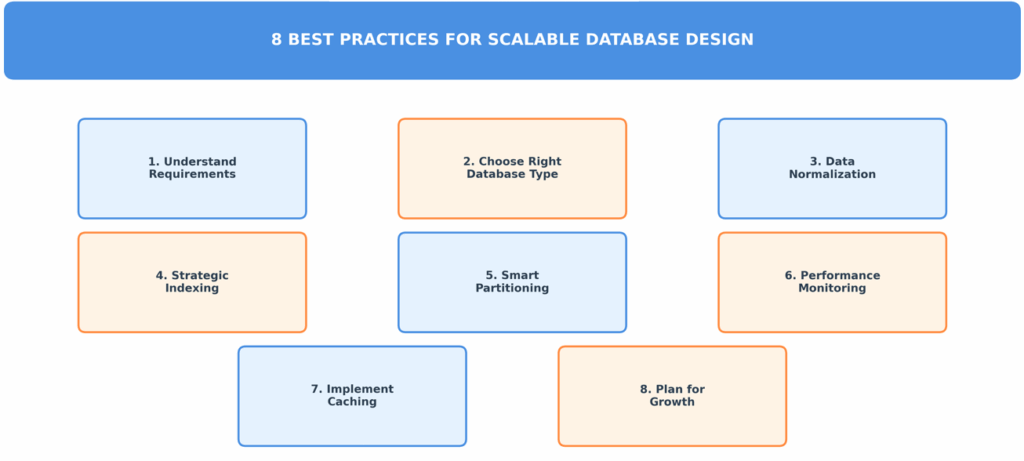
Best Practices for Database Design for New Applications
Our expert developer team is here to help you develop a swift database for your systems. Follow these implemented practices for better performance of your applications.
Understanding Your Requirements
First of all, you need to understand the requirements of your applications. You must know the amount of data you will be handling. Find out if your applications perform an increased rate of read and write operations.
You need to understand how users will access the data. Determine the response time to know the performance output of your applications.
Choose a Suitable Database
Choosing the right type of database is the first thing to do after knowing your requirements. Here are two main types to look into:
- Relational Database’s(RDBMS):
It is perfect for those applications that require ACID(Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) attributes and complex inquiries. For understanding, take the example of MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL.
- NoSQL Database:
It is suitable for applications that have unstructured data and require high scalability. Its types include CouchDB, Cassandra, HBase, and more.
Normalization of Data
Normalization of data means to organize it to reduce repetitions and improve its integration. There are some basic forms of normalization:
- First Normal Form(1NF):
It ensures each table has a primary key and no repeating groups.
- Second Normal Form(2NF):
Second Normal Form is a database normalization step that builds on 1NF to make a cleaner and more efficient table.
- Third Normal Form(3FN):
Third Normal Form has no transitive dependencies and it means no non-primary key attribute should depend on another non-primary key attribute.
It is a fact that normalization of data can reduce repetitions, but it can sometimes increase complexities and performance issues. Therefore, it is necessary to build a balance between normalization and denormalization.
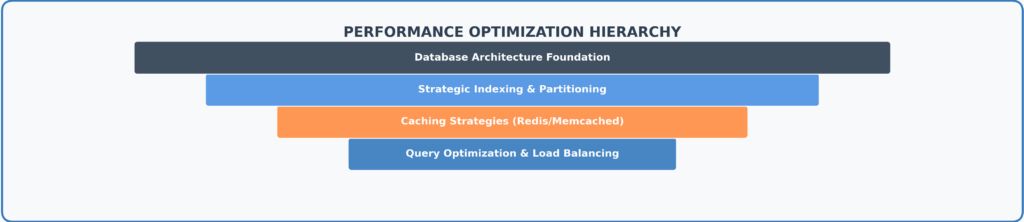
Use Indexes Strategically
By using indexes, you can speed up data retrieval but it can slow down the writing tasks and increase storage requirements. Its key consideration includes primary, secondary, and composite indexes.
Primary indexes are essential for uniquely identifying rows. Secondary indexes speed up query operations on non-key columns, and composite indexes are beneficial for queries having multiple columns.
It is crucial to monitor and optimize indexes on query performance and access patterns.
Partitioning
Partitioning involves dividing large databases into smaller and manageable pieces without disturbing the logical structure. There are three main types of partitioning:
- Horizontal partitioning(Sharding)
- Vertical partitioning
- Range partitioning
With the help of partitioning, you can distribute the load and enhance the manageability of the applications.
Monitor Performance
One of the main steps of database scalability is to monitor and optimize the database performance. It includes three main practices:
- Query Optimization
Optimize slow queries using tools like EXPLAIN in SQL.
- Regular Maintenance
Routine maintenance should be followed, like analysing tables, vacuuming, and rebuilding indexes.
- Load Balancing
It means distribution of data across multiple servers to prevent any single server from crashing.
Implementing Caching
By introducing coaching, you can reduce the load as it temporarily stores data in the memory. Use these strategies:
- Application-Level Caching
Cache data within the application’s memory.
- In Memory Caching
Use data storage systems like Redis or Memcached.
- Database Caching
Use built-in database caching mechanisms.
You should choose the right caching strategy according to your application.
Plan to Enhance the System
You should implement testing and trials to understand how the database performs. Use solutions that allow seamless scaling up and down according to demand. Make changes for the growth and development of scalable applications.
Next Steps for Scalable Architecture
Setting up scalable database design patterns is necessary to build a strong architecture for long-term success. By following our strategies and best practices, such as choosing suitable databases, normalizing, partitioning, implementing caching, and planning for growth, you can build scalable databases for your applications.
A well-planned database ensures that the database architecture remains flexible and undisturbed when the application grows. You need to do regular testing, reviews, and maintenance to keep high performance and security standards. Follow up with us for more tech updates and the growth of your apps!